Introduction
Gynecomastia, a condition often shrouded in physical discomfort and emotional turbulence, manifests as an enlargement of the glandular tissue in the male breast. Recognising the symptoms and signs of Gynecomastia not only paves the way for early intervention but also aids in navigating through potential psychological implications. While the common condition of breast enlargement often remains under-discussed, awareness of its symptoms and signs is crucial for timely diagnosis and management.
Understanding Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia, derived from the Greek words ‘gyne’ meaning ‘woman’ and ‘mastos’ meaning ‘breast’, is a condition characterised by the enlargement of breast tissue in males. It is not merely a cosmetic concern but also a potential physical and psychological discomfort source. The prevalence of Gynecomastia spans across all age groups, with notable spikes during periods of hormonal fluctuations such as infancy, adolescence, and later adulthood. The causes are multifaceted, ranging from hormonal imbalances, where an increase in estrogen levels or a decrease in testosterone occurs, to underlying health conditions and, in some instances, certain medications or the use of anabolic steroids.
Identifying Symptoms of Gynecomastia
The symptoms of Gynecomastia extend beyond the physical realm, intertwining with emotional and psychological facets. Physically, individuals may notice a rubbery or firm mass extending concentrically from the nipples, potential breast pain or tenderness, and sometimes, nipple discharge. The emotional impact, however, is often veiled behind the physical symptoms. Men and boys with Gynecomastia frequently experience emotional distress, body image issues, and, in some instances, social avoidance, particularly in situations that require exposing the chest, such as swimming. While not visible, the psychological symptoms are equally significant and warrant attention and empathy.
Physical Signs of Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia presents itself through various visible and palpable signs that can be discerned upon a physical examination. The most conspicuous sign is the enlargement of the male breast with fatty tissue, which may be symmetrical or asymmetrical. Palpable signs include a rubbery or firm breast bud mass extending concentrically from the nipples. It’s pivotal to differentiate Gynecomastia from other conditions, such as pseudogynecomastia, which is characterised by an increase in adipose tissue rather than glandular tissue, and breast cancer, which may present as a lump in one breast, nipple retraction, or skin changes. The differentiation is crucial as it steers the course of management and treatment.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
The emotional and psychological effects of Gynecomastia can be profound and far-reaching. Men and boys with this condition often grapple with feelings of embarrassment, self-consciousness, and a diminished sense of masculinity. These emotional effects can cascade into broader aspects of life, affecting social interactions, self-esteem, and mental well-being. The importance of mental health cannot be overstated, and support from family, friends, and professionals is paramount. Engaging in supportive dialogues, seeking counselling, and joining support groups can be instrumental in navigating through the emotional labyrinth posed by Gynecomastia.
Seeking Medical Attention
The journey towards addressing Gynecomastia commences with seeking medical attention. Consulting a healthcare professional is vital when physical signs are noticed, pain or tenderness, breast swelling and breast tenderness is experienced, or when the emotional impact becomes burdensome. During a medical consultation, one can expect a thorough physical examination, a detailed discussion about medical history, and, potentially, further diagnostic tests such as mammograms or ultrasounds. The healthcare professional will explore Gynecomastia’s physical and psychological impact on the individual, guiding them through the available management and treatment options and potentially offering referrals to specialists or support groups.
Diagnostic Procedures
Embarking on the path toward an accurate diagnosis of Gynecomastia necessitates a thorough and meticulous approach to diagnostic procedures. The initial step typically involves a comprehensive physical examination and a detailed discussion regarding the individual’s medical history, symptom onset, and potential drug use. Subsequent to this, diagnostic tests are employed to further elucidate the condition and rule out other potential causes. These may encompass blood tests to evaluate hormone levels like testosterone levels, mammography, or breast ultrasound to visualise the breast tissue, and in certain instances, a biopsy to confirm the nature of the glandular tissue. An accurate diagnosis is paramount, as it confirms Gynecomastia and ensures that any underlying causes or similar conditions are identified and aptly addressed.
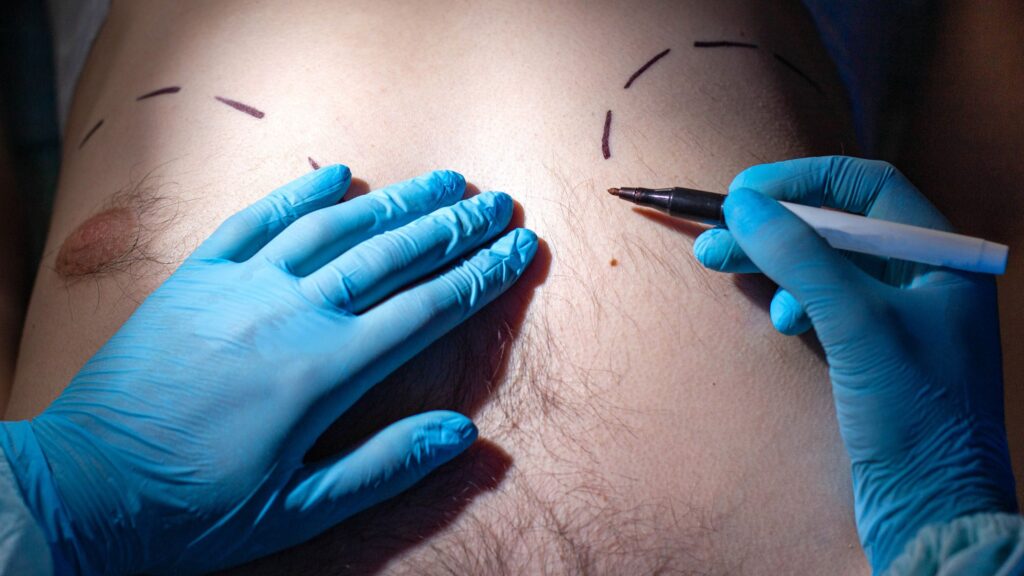
Treatment Of Gynecomastia
Navigating through the myriad of treatment options for Gynecomastia involves a thorough exploration of both surgical and non-surgical avenues. The selection of treatment is often influenced by the underlying cause of Gynecomastia, the degree of physical discomfort, and the psychological impact experienced by the individual. Non-surgical treatments may encompass hormone therapy or medication to address any underlying hormonal imbalance or to reduce breast size. On the surgical front, options include liposuction, which involves the removal of breast fat, and mastectomy, which entails the removal of the breast gland tissue. Both surgical and non-surgical treatments possess their own set of advantages and potential risks, which should be meticulously discussed with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable course of action.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive exploration of Gynecomastia, we have traversed through its multifaceted dimensions, shedding light on its symptoms, signs, and the subsequent paths toward diagnosis and treatment. Gynecomastia, characterised by an enlargement of the male breast tissue, manifests through various physical and psychological symptoms, each wielding its own set of challenges and impacts on an individual’s well-being. The journey from recognising the initial symptoms through the labyrinth of diagnostic procedures to exploring treatment options is deeply personal and unique to each individual. It is imperative to underscore the significance of seeking professional help, as a healthcare professional or specialist can provide a tailored approach, ensuring that the chosen path of management and treatment is congruent with the individual’s physical and emotional needs.
FAQs/Additional Tips
Q: Can Gynecomastia resolve on its own? A: Gynecomastia may resolve without intervention in certain instances, particularly during puberty. However, persistent or bothersome symptoms warrant a consultation with a healthcare professional.
Q: Is surgery the only option for treating Gynecomastia? A: No, treatment options are varied and can include non-surgical approaches such as medication or hormone therapy, depending on Gynecomastia’s underlying cause and severity.
Q: Can exercise reduce Gynecomastia? A: While exercise can aid in overall weight loss, it cannot specifically target glandular tissue enlargement, which is characteristic of Gynecomastia.
Additional Tips:
- Engage in open dialogues: Discussing your symptoms and emotional experiences with loved ones or a support group can provide emotional relief and additional perspectives.
- Wear comfortable clothing: Opting for clothing that provides physical comfort and minimises any potential self-consciousness can be beneficial.
- Explore professional forums: Engaging in forums or groups led by healthcare professionals can provide credible information and support.
